What is a Complete Blood Count (CBC) Blood Test?

A Complete Blood Count, commonly called a CBC blood test, is one of the most frequently ordered laboratory tests. Doctors use this test to measure different components of your blood and to get a general picture of your overall health.
The main purpose of a CBC is to determine the concentration and condition of various cells found in the bloodstream. These include:
- Red blood cells
- White blood cells
- Platelets
Most CBC tests are performed using automated laboratory machines that analyze the blood sample within a few minutes. The results provide valuable information about oxygen levels, immune function, and clotting ability.
A CBC is often part of routine checkups, but it is also ordered when someone has symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, fever, bruising, or unexplained bleeding.
What Method is Used for the CBC Blood Test?

The CBC blood test requires a small blood sample, usually one to three tablespoons. This sample may be taken specifically for the CBC or obtained from blood that was already collected for other tests.
Blood collection can take place in several settings, including:
- Doctor’s offices
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic laboratories
- Phlebotomy centers
During the procedure:
- The healthcare professional cleans the skin with alcohol to prevent infection.
- A visible or palpable vein is located, usually in the arm.
- A needle is gently inserted into the vein.
- Blood is drawn into a syringe or vacuum tube.
- The sample is sent to the laboratory for analysis.
The entire process usually takes only a few minutes and causes minimal discomfort.
A Complete Blood Test
The CBC is sometimes referred to simply as a “complete blood test” because it evaluates many important blood components at once. It gives doctors a broad overview of your blood health and helps guide further testing if abnormalities are found.
CBC Blood Test
The CBC blood test measures several key values related to red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These values help doctors detect infections, anemia, inflammation, and other medical conditions.
What does the CBC Blood Test Indicate, and What Does It Test For?
The CBC blood test examines the following components:
White Blood Cell Count (WBC)
This measures the number of white blood cells in a volume of blood. White blood cells help fight infection.
- Normal range: approximately 4,300 to 10,800 cells per cubic millimeter
- Also called the leukocyte count
White Blood Cell Differential Count
This breaks down the total white blood cell count into specific types:
- Neutrophils (granulocytes)
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
Each type is reported as a percentage and helps identify infections, allergies, or immune disorders.
Red Blood Cell Count (RBC)
This measures how many red blood cells are present in your blood.
- Typical range: 4.2 to 5.9 million cells per cubic millimeter
- Also called the erythrocyte count
Red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body.
Hemoglobin (Hb or Hbn)
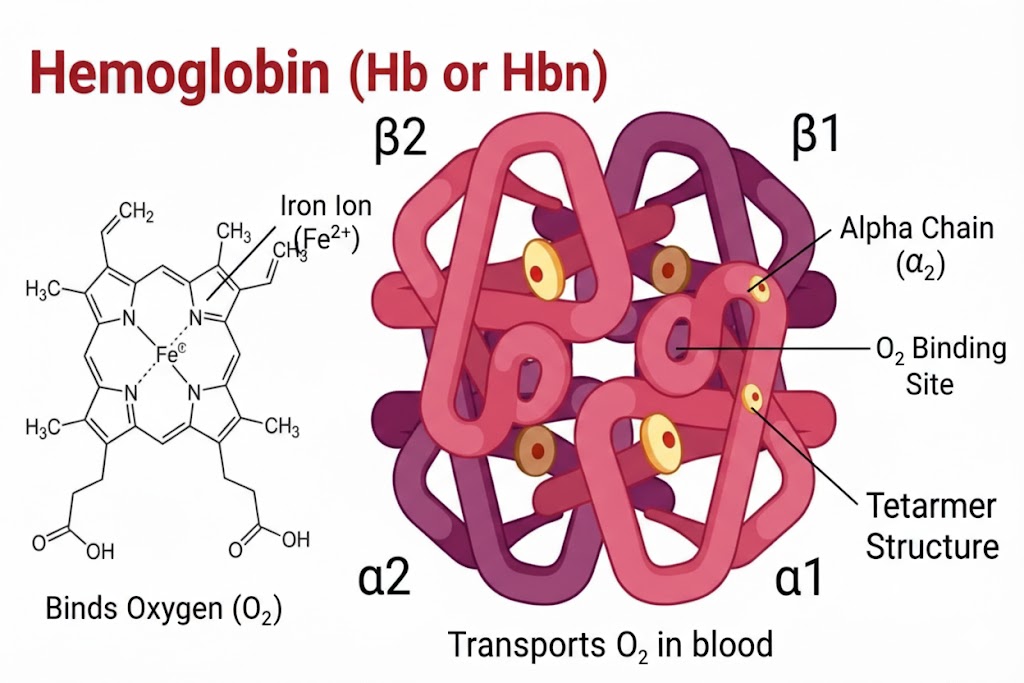
Hemoglobin is the protein inside red blood cells that transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carries carbon dioxide back to the lungs.
- Normal range for men: 13 to 18 g/dL
- Normal range for women: 12 to 16 g/dL
Low hemoglobin often points to anemia.
Hematocrit (Hct)
This shows the percentage of blood made up of red blood cells.
- Men: about 45–52%
- Women: about 37–48%
It is measured by spinning blood in a centrifuge to separate cells from plasma.
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
This reflects the average size of red blood cells.
- Helps classify anemia
- Normal range varies by lab
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH)
This indicates the average amount of hemoglobin in each red blood cell.
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC)
This measures how concentrated hemoglobin is inside red blood cells.
- Normal range: approximately 32–36%
Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW)
This measures variation in red blood cell size and shape.
- Normal range: about 11–15
- Higher values suggest uneven cell sizes
Platelet Count
Platelets help blood clot.
- Normal range: 150,000 to 400,000 per cubic millimeter
Mean Platelet Volume (MPV)
This shows the average size of platelets and gives clues about platelet production.
Complete Blood Count Examines
A CBC provides information about:
- Oxygen-carrying capacity
- Immune system activity
- Clotting potential
- Bone marrow function
- Signs of infection or inflammation
Complete Blood Count
Doctors often order a CBC as part of routine care or when symptoms suggest an underlying problem. It is widely used because it is fast, affordable, and informative.
What is the CBC Blood Test Used For?
The CBC helps identify many medical conditions, including:
- Infections
- Anemia
- Certain cancers
- Bone marrow disorders
- Bleeding disorders
- Severe inflammation
- Low blood oxygen levels
It is commonly ordered alongside other tests, such as liver or kidney panels, or during general health checkups.
Because it is relatively inexpensive, the CBC is frequently used as an early screening tool to detect health issues that might not be obvious during a physical exam.
How is a CBC Blood Test Done?
A trained healthcare professional cleans the skin, usually on the arm near the elbow, using an alcohol swab. This reduces infection risk.
They then:
- Locate a vein by sight or touch
- Insert a needle into the vein
- Collect blood into a syringe or vacuum tube
- Remove the needle and apply pressure
The sample is sent to a laboratory, where automated machines measure each blood component.
Most people can return to normal activities immediately after the test.




